On June 3, 2019, the new edition of FSSC 22000 was released. One of the triggers for the revision is the introduction of the ISO 22000: 2018 standard, which acts as the basis for certification recognized by the GFSI. The new version of FSSC 22000 brings structural changes in particular, which we present below.
We would like to start off by giving you an insight with regard to the structure of FSSC 22000. The standard is made up of three components: ISO 22000, PRPs and the additional FSSC 22000 requirements. The international standard ISO 22000 forms the structure of FSSC 22000 and outlines the requirements related to the development, implementation and maintenance of the food safety system. The requirements are set out in the ISO 22000:2018 standard.For this reason, the update of ISO 22000 also has a significant impact on FSSC 22000.With the sector-specific preventive programs (PRPs), FSSC 22000 ensures the mandatory application of technical specifications. This is to facilitate the prevention and/or reduction of contamination in products, product development and the working environment. The requirements for this are laid down in the ISO/TS 22002-x series, in NEN/NTA 8059 and/or in the BSI/PAS 221 standard. The additional requirements of FSSC 22000 address service management, product labeling, food safety, and food fraud prevention.
In the new version 5, there is a voluntary quality management module. The elements of ISO 9001 that can be integrated are included in this module in the FSSC 22000 certification. Thus, a food safety management certification can be performed together with a quality management certification.
FSSC 22000 is applied in the following industries: Food manufacturing, food packaging manufacturing, animal feed production and agriculture, transportation and warehousing, catering, and retail and wholesale. The GFSI benchmark applies to food manufacturing (food chain category C), animal feed (D), transportation and storage (G), packaging (I), and biochemicals (K).
Changes in version 5
One of the main triggers for the revision was the publication of the ISO 22000:2018 standard, which stipulates that all certifications based on the standard must be adapted to the revision within three years, no later than June 29, 2021. For FSSC 22000, ISO 22000 forms the basis, as mentioned above, so a revision was inevitable. The changes to ISO 22000 and thus also to FSSC 22000 are mainly structural. For completeness, we list the changes again below. You can also read about them in our article on the changes to ISO 22000.
Introduction of the High Level Structure: With the recently revised ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015, ISO 22000:2018 shares the High Level Structure, the uniform basic structure for management system standards. This will make ISO 22000 comparatively easy to incorporate into integrated management systems.
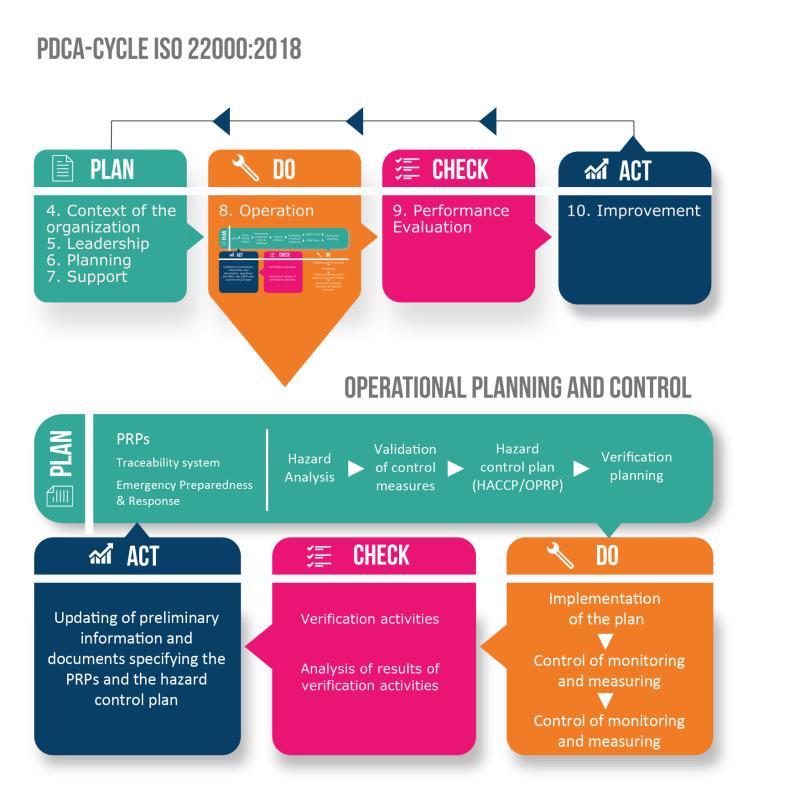
As is also the case with ISO 9001:2015 and ISO 14001:2015, ISO 22000:2018 stands for a risk-based approach. The standard distinguishes between risks at the operational level (HACCP approach) on the one hand, and risks at the management system level on the other - i.e., the risks that affect the ability of the management system to achieve its objectives.
The standard describes two different Plan-Do-Check-Act cycles: The first cycle forms the management system as such; the second cycle, which is embedded in the first, comprises the process steps depicted in clause 8 ("Operation"). The graphic below shows the two cycles and their interaction.
Furthermore, in FSSC 22000 version 5, new definitions have been added as well as additional information on the different categories. Requirements has been improved in the new version and they have used the revision to offer the integrated quality management system audit. Here you can download the revision of FSSC 22000 for free.
Timetable for the changeover
- Version 4.1 audits can still be performed until the end of December 2019 at the latest.
- The move to version 5 can be made at the time of a re-certification as well as at the time of a surveillance audit.
Changeover at the time of a re-certification: After a successful audit, a certificate according to version 5 is issued. The certificate is valid for three years.
Changeover at the time of a surveillance audit: The regular surveillance audit is replaced by an upgrade audit. After a successful upgrade audit, the existing certificate is replaced by a certificate according to version 5. The expiration date of the new certificate corresponds to the expiration date of the replaced certificate. - All upgrade audits must take place between January 1, 2020 and December 31, 2020. In exceptional cases, the upgrade audit may still be performed in 2021, by June 29, 2021. After this date, FSSC 22000 V4.1 certifications are invalid. Sites that have not upgraded to version 5 by this date will need to begin an initial assessment to regain certification.
- The first audit after version 5 is an announced audit
- After June 29, 2021, all V4.1 certificates will be set to invalid in the FSSC 22000 portal and will therefore no longer appear on the public list of certified companies.
DQS - Your partner for certification according to FSSC 22000 Version 5
DQS is one of the leading certification bodies for quality management systems and sustainability standards. We are at your side during the certification process - with smooth audit planning, experienced auditors and in-depth audit reports.
DQS Newsletter
Constanze Illner
Constanze Illner (she/her) is Research and Communications Officer in the area of sustainability and food safety. In this position, she keeps an eye on all important developments in this context and informs our clientele in a monthly newsletter. She also moderates the annual Sustainability Heroes conference.